What is Customer Journey?
Customer journey is the totality of experiences a customer has with an organization. It encompasses all customer interactions across all channels, devices and touch points throughout all stages of the customer lifecycle, from product awareness, service, company until becoming a loyal customer of the business.
Business owners can use this knowledge to better tailor their website design or marketing campaign materials to be more appealing or take advantage of new technology. A well-planned customer journey helps a business create an experience for customers that will help increase sales and loyalty.
What are the four stages of Customer Journey?
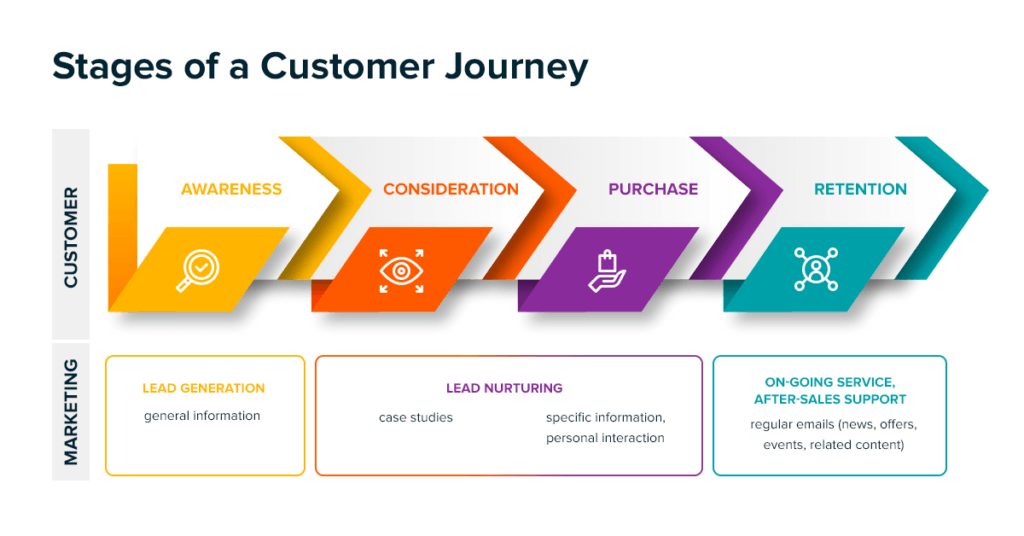


Stage 1: Awareness
Awareness is where the prospect is trying to formulate what the product or service is, or is even aware that it exists.
In marketing it is important to remember that your prospects are interested in themselves, what they need and solving their own problems. So you need to create a strong clear message with a great deal of information on it.
Remember that your prospects are not trying to buy from you; they’re trying to buy an answer. Make your offer simple, compelling and easy for them to understand.
Some strategies to attract prospects to your business through awareness are:
- Advertising and paying for a large distribution of your message.
- Writing a highly shareable blog post about your solution to a problem that your prospects are trying to solve.
- Being as clear and upfront about your offering as possible. Make sure it is easy for someone with no knowledge of what you do or how you do it to know exactly what you’re selling.
Stage 2: Consideration
Consideration, where your customer is researching similar products and options. The key to this stage is not just to give them the information they are looking for but also (and perhaps more importantly) the information that you want them to find.
Heuristics are used in this stage of customer decision making. These are mental shortcuts which people use when choosing how to behave. They can be invaluable when promoting your product or service because they give people a shortcut way of deciding whether they will take action on your proposition or not.
Some strategies related to consideration are:
- Understanding and accommodating the heuristics that prospective customers use during this stage. (For example, you can use hypothetical, specific examples of how your product or service could possibly solve the problem)
- Developing relationships with other businesses in the market which complement your offering. (You can sell some of their products or services to add value for their customers to increase their probability that they will purchase).
- Looking at how other industries solve similar problems. (For example, if you are a restaurant chain, check out how other restaurant chains get people to eat in their restaurants).
Stage 3: Decision
Decision, this stage is all about getting the customer to take a decision and is where your marketing and sales pitch needs to be most direct.
There are a number of ways you can do this:
- Have a clear offer with a limited time incentive attached.
- Show your customers the benefits of purchasing your product or service and how they will get a lot more than they expect.
- Make sure that you are using tailored content in your emails (or wherever else) to encourage people to take action when they receive it.
- Try and understand those customers that have decided against making a purchase. What is it that they are considering, and how can you address this?
- Offering statements of celebrity endorsement and giving clear instructions on how to take action (known as “click through” marketing). It’s during this stage that the prospect begins to feel that they have made a good decision.
Stage 4: Engagement
Engagement, where the customer uses your product or service for the first time and can then be turned into an advocate for your business through word of mouth marketing.
Some strategies related to engagement stage are:
- Ensure you have a great support team who the customer can use if they have any problems.
- Listen to the customer’s feedback and make improvements based on that.
- Provide them with related products or services which would be of benefit to them. (For example, if they bought a car from you, then they may also be looking for car insurance or accessories). You could offer them an incentive to buy these products by bundling it with your original product offering).
How to build a customer journey map
A customer journey map is a graphic that is used to visualize and understand customer journeys in the context of business. It is created with a combination of the customer-centric point of view and data from a range of analytics sources, including web and mobile analytics, surveys, financial data etc.
Step 1: Set goals
The first step in any process is to define the end goal. What you want to achieve with your customer journey map, and how your business will operate.
Step 2: Conduct persona research
Your customer journey map is only as good as the research behind it, so be sure to account for persona research. Personas help you to understand exactly who your key audiences are and what their needs are.
Persona research should be conducted in order to identify specific aspects of your customers’ experience that need improvement. For example, you’ll want to know the challenges they face when trying to place an order—or where they have a difficult time finding their way around your site.
The aim is to identify specific issues that need to be addressed in order to improve the customer experience, and then prioritize these aspects accordingly.
It’s important to be able to run new user research for personas once your business has been up and running for some time. This will help you understand how users are actually using your app and website at any given time, so you can create a more accurate customer journey map as you go.
You can gather data in any of the following ways:
- Website analytics
- User surveys
- User interviews
- Track social media channels for user feedback
- Mobile customer journeys
Step 3: Define customer touch points
At each stage of the customer journey, you should have a clear and precise idea of what is expected from customers, who they are and what parts of your digital product are currently working well.
To understand your customer touchpoints, look at the actual moment you interact with customers. Separate all content into distinct categories and explore all of the various touchpoints that you have available to smooth out the customer experience.
These touchpoints can include types of content, like product descriptions, in-app messages and CTAs, along with the navigation of your site or app. Your customer journey map needs to be completely clear when it comes to identifying what exactly a customer will see and how they will interact with each step.
Step 4: Map the current state
Based on your research, create a visual representation of the current customer journey.
To do this, look at the data first to identify any pain points that are happening during each stage of the customer experience. For example, if you’ve discovered certain drop-off points or areas where users have questions about a product, you’ll want to include those in your customer journey map for consideration when it comes to improvement.
Once you’ve created your customer journey map, use it as a tool to identify any opportunities for improvement. This could include anything from simplifying the flow of information, finding a better way to display content or testing out new messaging.
Once you’ve identified areas of improvement, you can then decide on how to respond.